What is CNC machining and how does it work?
- Start Date:- 2025-05-26
- End Date:- 2027-09-30
- Start Time:- 00:02:00
- End Time:- 11:07:00
Event Information :
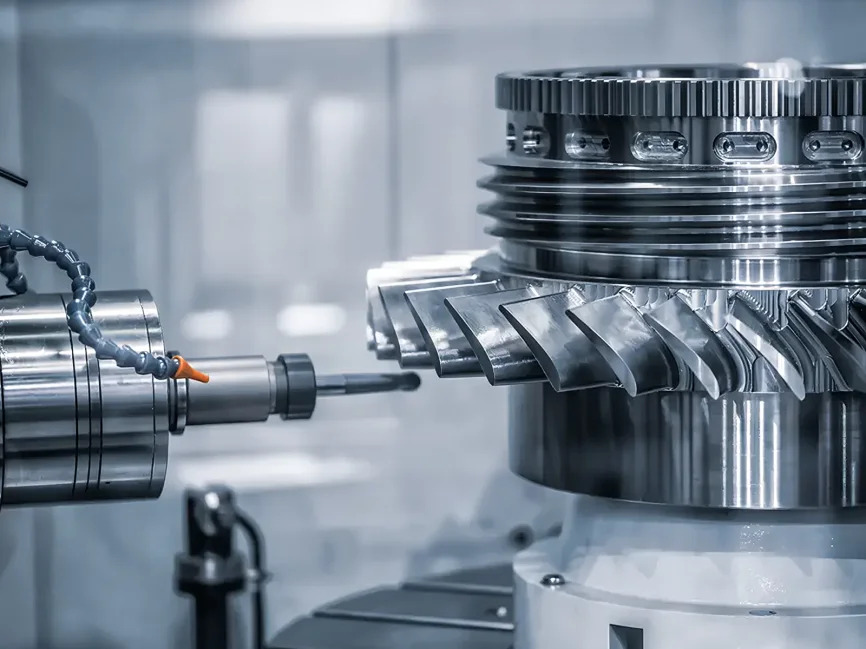
CNC machining, short for Computer Numerical Control machining, is a manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to control the movement of factory tools and machinery. A CNC machining service uses this technology to automate the production of complex parts with high precision and consistency, making it a cornerstone in modern manufacturing.
How CNC Machining Works
At the heart of CNC machining is a digital design file, usually created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This file is converted into a set of instructions, called G-code, which tells the CNC machine how to move, cut, drill, or shape the material. Once the G-code is uploaded to the CNC machine, it performs the operations automatically, with minimal human intervention.
CNC machines can operate on multiple axes, typically ranging from 3 to 5, which allows for intricate designs and complex geometries. Common types of CNC machines include CNC milling machines, CNC lathes, and CNC routers. Each type is specialized for different kinds of operations—milling involves rotating tools that remove material, while lathes rotate the workpiece itself against a stationary cutting tool.
Materials Used
CNC machining is compatible with a wide variety of materials, including metals such as aluminum, steel, titanium, and brass, as well as plastics like ABS, nylon, and polycarbonate. The flexibility in material selection makes CNC machining suitable for industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to medical and consumer electronics.
Advantages of CNC Machining
One of the key advantages of CNC machining is its precision. Machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances, making them ideal for parts that require exact specifications. CNC machining is also highly repeatable, which ensures consistency across large production runs. Additionally, the process is efficient and scalable, allowing for both rapid prototyping and full-scale production.
Applications
CNC machining is used to manufacture parts and components for countless products and industries. In aerospace, it produces high-performance engine parts and structural components. In the medical field, it creates surgical tools and implants. Automotive companies use it for engine blocks, transmission housings, and more. The versatility of CNC machining makes it a go-to solution for manufacturers worldwide.
Conclusion
CNC machining is a powerful and versatile manufacturing process that combines digital technology with precision engineering. By automating the control of machinery through computer programming, CNC machining delivers fast, accurate, and repeatable results across a broad range of materials and applications. Whether for a single prototype or high-volume production, CNC machining continues to play a vital role in modern industry.
Register at
Free
What is CNC machining and how does it work?
- Start Date:- 2025-05-26
- End Date:- 2027-09-30
- Start Time:- 00:02:00
- End Time:- 11:07:00

Event Information :
CNC machining, short for Computer Numerical Control machining, is a manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to control the movement of factory tools and machinery. A CNC machining service uses this technology to automate the production of complex parts with high precision and consistency, making it a cornerstone in modern manufacturing.
How CNC Machining Works
At the heart of CNC machining is a digital design file, usually created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This file is converted into a set of instructions, called G-code, which tells the CNC machine how to move, cut, drill, or shape the material. Once the G-code is uploaded to the CNC machine, it performs the operations automatically, with minimal human intervention.
CNC machines can operate on multiple axes, typically ranging from 3 to 5, which allows for intricate designs and complex geometries. Common types of CNC machines include CNC milling machines, CNC lathes, and CNC routers. Each type is specialized for different kinds of operations—milling involves rotating tools that remove material, while lathes rotate the workpiece itself against a stationary cutting tool.
Materials Used
CNC machining is compatible with a wide variety of materials, including metals such as aluminum, steel, titanium, and brass, as well as plastics like ABS, nylon, and polycarbonate. The flexibility in material selection makes CNC machining suitable for industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to medical and consumer electronics.
Advantages of CNC Machining
One of the key advantages of CNC machining is its precision. Machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances, making them ideal for parts that require exact specifications. CNC machining is also highly repeatable, which ensures consistency across large production runs. Additionally, the process is efficient and scalable, allowing for both rapid prototyping and full-scale production.
Applications
CNC machining is used to manufacture parts and components for countless products and industries. In aerospace, it produces high-performance engine parts and structural components. In the medical field, it creates surgical tools and implants. Automotive companies use it for engine blocks, transmission housings, and more. The versatility of CNC machining makes it a go-to solution for manufacturers worldwide.
Conclusion
CNC machining is a powerful and versatile manufacturing process that combines digital technology with precision engineering. By automating the control of machinery through computer programming, CNC machining delivers fast, accurate, and repeatable results across a broad range of materials and applications. Whether for a single prototype or high-volume production, CNC machining continues to play a vital role in modern industry.
Register at

